Updating to Windows 11 promises smoother performance, better security, and a sleeker interface. However, to some users, this move instead becomes a nightmare when all valuable files suddenly disappear after the update. You do your update, log back in, find an empty desktop, no folders, and nothing in your Documents library.
In case it happened to you, do not worry, as there are some alternative ways to recover lost files after Windows 11 update without having to use costly tools or services. This tutorial will mention the reasons and provide you with free ways you can restore your data fast and safely.
Part 1: Why Did Windows 11 Update Delete My Files?
Upgrades are supposed to be safe and secure. However, in practice, different bugs, incorrect settings, or misaligned system configurations during a big Windows update hide or even delete user data.
There are a lot of user reports that the Windows 11 update deleted their files. This could happen due to a number of reasons, so let us analyze them one by one:
1. Windows 11 Logged You into a Temporary Account
Windows logging you into a temporary user profile rather than your regular account is one of the most prevalent issues after an update.
You will see that something is wrong, your desktop background is missing, files are lost, and programs that you have installed are reset. This is sometimes carried out by Windows when it experiences profile loading problems. They are still stored on the drive and are linked to your original user folder. To check:
- Go to C:\Users\ and find another folder that may look like your old username.
- Provided it exists, then your files are probably still there but associated with another profile.
2. Insufficient Disk Space
If your system lacked sufficient free disk space prior to installation of the update, Windows might have removed temporary files, cached data, and in extreme instances, even non-system personal files. To install the update, a minimum of 64 GB of free space is needed, and it is preferable to have a buffer of 15-20% of the drive to prevent such problems.
Windows may also relocate data to clear space using Storage Sense or remove old copies of files, particularly in the Downloads or Temp directories.
3. Corrupted User Profile
A damaged user profile may disrupt the connection between Windows and your personal information. It is possible to log in and not see files or apps. In other cases, the corruption may take place during an update process or during a migration of user settings.
This corruption may hide or lock access to your own documents, even though they physically exist on the drive.
4. Failed Partition Conversion
Some systems convert to a partition type during update, particularly between legacy BIOS to UEFI. In case that process fails or has problems (because your drive has been formatted or misaligned), your drive can become partially inaccessible, and partitions can become corrupted, resulting in the loss of data.
5. Failed Update Process
A partial or failed upgrade can occur during an update due to a power loss, force shutdown, or hardware failure. In such scenarios, the system can be recovered to a semi-active state where some of the system files have been updated, and in that process, you lose or cannot access your data.
6. Third-party Software Conflict
The Windows update process may be disrupted by some antivirus software, optimization programs, or system cleaners.
They may obstruct or cut off key system processes, resulting in unsuccessful migrations of profiles and skipping the file retention process.
After the update, they could proceed to quarantine or delete files that were falsely labelled as “temporary” or “orphaned”.
Part 2: How to Recover Lost Files After Windows 11 Update
The good thing is that lost files after Windows 11 update can usually be restored, especially if you act quickly. The following are six tested ways that can help you recover your files.
- 1. Find Lost Files Using Search
- 2. Restore Lost Files from Backup
- 3. Enable the Administrator Account
- 4. Check the Recycle Bin
- 5. Recover Lost Files Using File History
- 6. Using Third-party File Recovery Software
1. Find Lost Files Using Search
Before moving to a complex and sophisticated recovery method, you should start with the easiest, which is simply just searching with the instructions below:
- Open File Explorer, click on This PC, and search for the lost documents using the search bar.
- Search by file type (e.g., .docx, .jpg) or file name in case you can recall it.
- Navigate to the File Explorer as View > Show > Hidden items to reveal all the hidden folders or files that could have been hidden during the update.
- Also, check the places such as C:\Windows.old, which might have your old files before the upgrade.
2. Restore Lost Files from Backup
In case you had activated backup facilities like File History, Windows Backup, or even cloud sync (like OneDrive), this is how to restore your data:
- Backup and Restore: If you have created a backup on an external drive using the Backup and Restore (Windows 7) feature, then you can connect the drive to the computer to restore your files.
- System Image: In case you had stored a system image earlier, you will be able to boot into Windows Recovery Environment and restore your system from this backup.
- OneDrive or Google Drive: Log in and see whether your files have been synced prior to the update. You can possibly restore through your cloud archive.
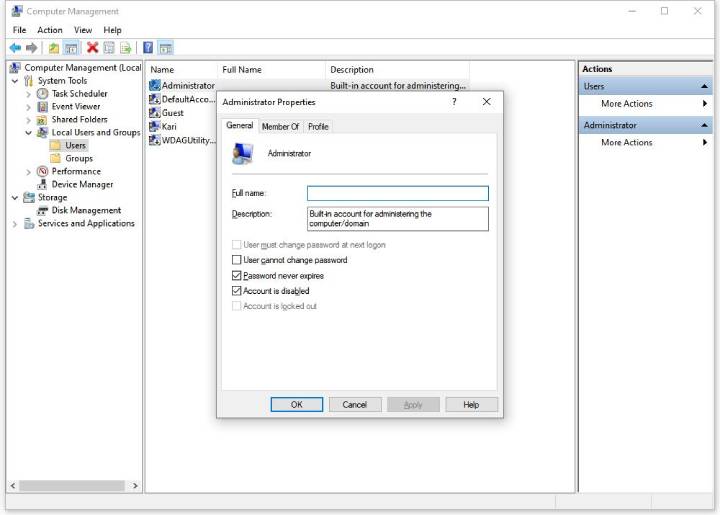
3. Enable the Administrator Account
If you create a new Microsoft account during the Windows 11 update process, your files may be stored in a disabled Administrator account. Here is how to enable the account and get the files back:
- Hit Win + X, then select Computer Management.
- Go to Local Users and Groups > Users.
- Double-click Administrator > uncheck Account is disabled > Apply.
- Log off and log on as an Administrator.
- Check out this location C:\Users\ and see if you have folders containing your old files.
- This trick can expose the user folder and documents related to earlier profiles.
4. Check the Recycle Bin
Occasionally, updates do a system-wide cleanup, and the files might not be deleted but instead transferred to the Recycle Bin. Open the Recycle Bin on the desktop and check whether the names of familiar files are available.
In case they are found, just right-click on them and then click on Restore to restore them to the original place. Just don’t go ahead and right-click on the Recycle Bin and empty it until you know your files aren’t there.
5. Recover Lost Files Using File History
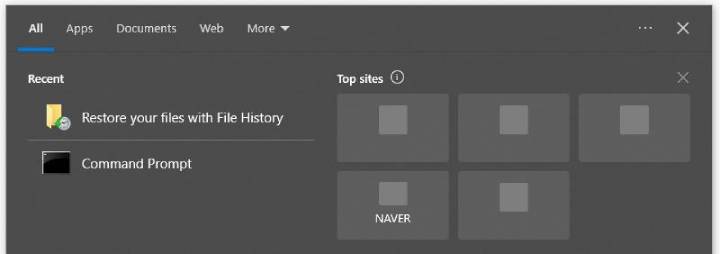
One of the most dependable built-in features to recover deleted files is File History, which you can do so by following the steps below:
- Search Restore your files with File History.
- Choose the option Restore personal files.
- View the list of versions and find the required document or folder.
- Tap on the green Restore button.
- File History stores previous versions of files, thus you may restore even files that were created or updated before the update.
6. Using Third-party File Recovery Software
In case none of the above is effective, you’d still have options. Such programs as iToolab RecoverGo Windows Data Recovery may search your drive and can help if you’re wondering how to recover deleted files after installing Windows 11. They come in handy in case you accidentally deleted the file or the partition table was messed up.
One more thing, you should never start storing files on the affected drive. There will be a possibility that the parts in which your old files are stored will be overwritten by every new file you create.
The main characteristics of iToolab RecoverGo Windows Data Recovery:
- Restore photos, documents, videos, and other important file types.
- Recover data from hard drives, SD cards, USB drives, and more storage devices.
- Successfully recover deleted files with a 99% success rate.
- Restores files even after emptying the recycle bin by mistake or accident.
To get started with iToolab RecoverGo, follow these simple steps to scan and retrieve your lost files efficiently.
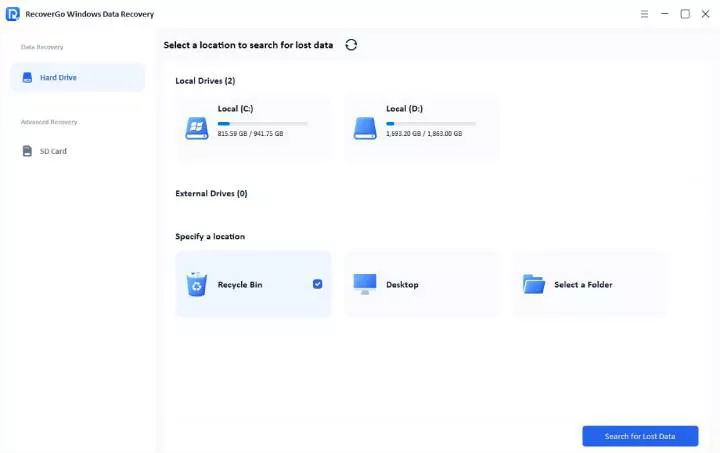
Step 1 Select a location
Launch RecoverGo and select the specific drive or folder where your data was lost. Once selected, click the “Search for Lost Data” button to prepare for the scanning process.
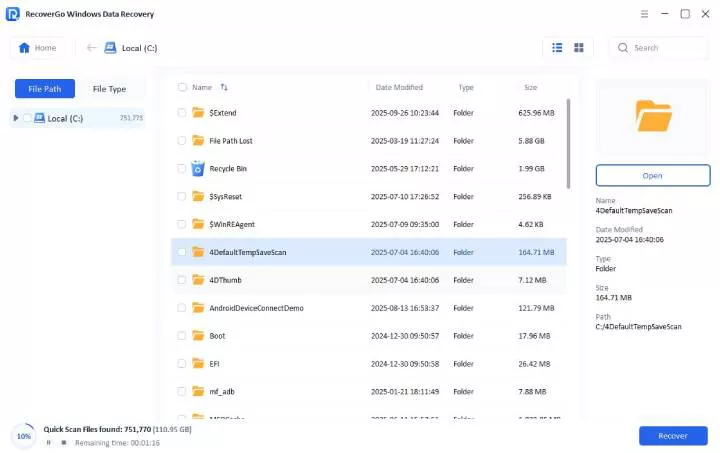
Step 2 Quick scan your device
The software will perform an advanced scan of your device to identify all recoverable files. You can filter the results by file type as they appear.
Step 3 Recover your data
Click “Check Found Files” to verify the file content. Finally, select the files you need to recover and save them to a different secure drive to avoid data overwriting.

Part 3: How to Avoid Data Loss After Windows Update
After restoring your files, use the following free and practical tips to defend yourself in future updates.
1. Make Regular Backups
Turn on Windows’s built-in backup feature, or frequently back up your important data to an external drive.
2. Maintain at Least 15-20 Percent Free Disk Space
The system drive should be empty in order to update. When installing a big update, leave at least 20 GB of free space.
3. Pause or Stage Updates
Utilize Windows update settings to postpone major updates. This provides time to jump in to catch bugs.
4. Turn off Antivirus/Optimization Programs Temporarily
Sometimes, an Antivirus, a third-party, or the native Windows defender, can do more harm than good. Avoid any conflicts by switching them off during the update.
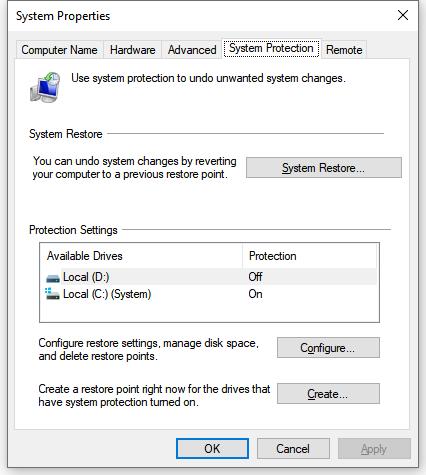
5. Create System Restore Point
Prior to every major update. Try the following:
Control panel > System> System Protection> Create a restore point
6. Use Test Environments or Create a Disk Image
Before updating, you should back up your disk image. Programs such as Disk2VHD will allow you to virtualize your existing configuration and test the update in advance.
7. Monitor Hard Disk Status
Check whether it is possible to run chkdsk or SMART before updates. When a drive fails, the chance of corrupting files is high.
Conclusion
When data gets lost during an update on Windows 11, it is quite stressful, but fortunately, there is usually a way to recover the data as long as you act fast. Use backups or recovery tools, check hidden folders, and search your system fully. In the worst case, recovered files may be retrieved using good free software.
Among these options, iToolab RecoverGo Windows Data Recovery is highly recommended as a powerful solution for quickly scanning and retrieving lost data after the Windows 11 update.

